When you see the status “Discovered – currently not indexed” in Google Search Console, it means that Google is aware of your URL but hasn’t crawled or indexed it yet. This often happens when Google is prioritizing other URLs or encounters obstacles accessing your page.
Google Search Console Indexing Issue: What It Is and How to Fix It
Common Reasons for “Discovered – Currently Not Indexed”
1. Low-Quality Content
Pages with thin, duplicate, or low-value content may be skipped during indexing. If your page doesn’t offer unique or useful information, Google may decide not to index it.
Example:
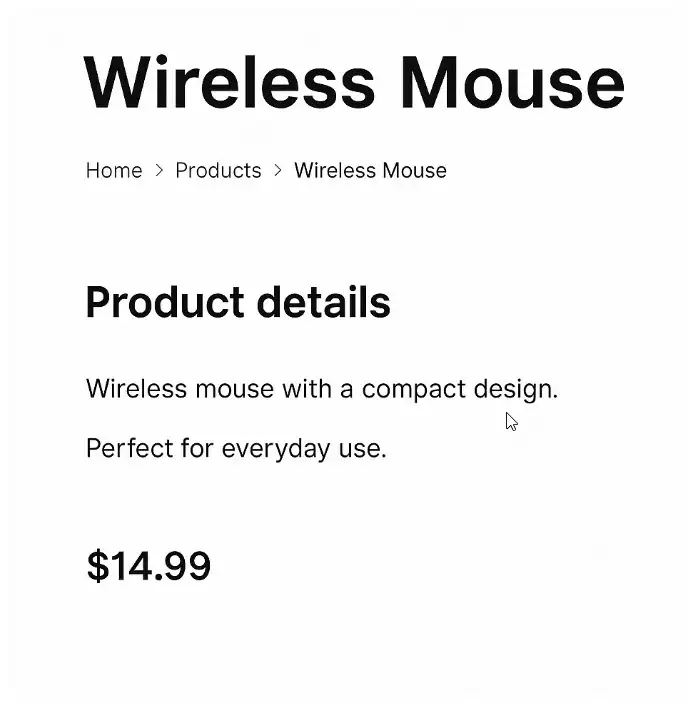
An online electronics store in the U.S. creates dozens of product pages, each containing only the product name and a short, generic description. These pages offer little value beyond what’s already available on other sites, so Google might ignore them.
2. Technical Issues
Problems like errors in the robots.txt file, “noindex” meta tags, or unclear site structure can prevent Google from crawling your pages.
Example:
A consulting agency in London accidentally blocks key service pages in its robots.txt file. As a result, Google is aware of the URLs from the sitemap but is unable to access and index them.
3. Poor Internal Linking
Pages that are not linked from other areas of your website may not be seen as important, making it harder for Google to crawl and prioritize them.
Example:
A blog in Canada publishes a new article but forgets to link it from the homepage, category pages, or other posts. Google may discover the URL via the sitemap, but without internal links, it may not consider the page significant enough to index.
4. Slow Page Load Speed
If your pages load slowly, Googlebot may abandon the crawl before finishing. Page speed is not just about SEO—it also affects user experience and engagement.
Example:
A photography portfolio in Australia features high-resolution images but doesn’t compress them. The result: slow-loading pages that Googlebot may delay indexing or skip entirely.
5. Limited Crawl Budget
Large websites with thousands of URLs may exceed Google’s allocated crawl budget, meaning not all pages get crawled or indexed.
Example:
An international news site publishes hundreds of articles daily. Without proper crawl management (like internal linking or sitemap segmentation), Google may delay or skip indexing some new articles due to budget constraints.
How to Fix It
1. Improve Content Quality
Ensure every page offers unique, relevant, and valuable content. Avoid thin or duplicate pages.
Tip:
Instead of just listing a product like “Wireless Mouse – Black,” include a detailed description, use cases, specifications, comparison with similar models, and customer reviews.
2. Check for Technical Errors
Use tools like Google Search Console or Screaming Frog to detect issues in robots.txt, meta tags, or overall site structure.
Checklist:
-
Don’t block important URLs in
robots.txt -
Remove unnecessary “noindex” tags
-
Ensure the page returns a valid 200 HTTP status code
3. Strengthen Internal Linking
Link to new or unindexed pages from your homepage, categories, or related content to signal importance to Google.
Example:
If you publish a new service page, make sure it’s accessible via your site menu, blog posts, or a relevant landing page.
4. Optimize Page Speed
Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Lighthouse to test and enhance loading speed.
Quick Fixes:
-
Compress large images
-
Minify CSS/JS files
-
Use browser caching
-
Consider a CDN for global users
5. Submit Indexing Requests
After resolving content and technical issues, use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to request indexing.
Note:
Submitting a URL does not guarantee immediate indexing, but it can help bring it to Google’s attention—especially if the content is new or recently improved.
Conclusion
The “Discovered – currently not indexed” status is a signal—not a penalty. It means Google has seen your URL but hasn’t committed to indexing it yet. This could be due to content quality, technical restrictions, weak internal linking, slow performance, or crawl budget limitations.
Understanding the causes and applying the fixes above will help ensure your pages get indexed, increasing visibility and improving SEO performance.

Hi, I’m Nghia Vo: a computer hardware graduate, passionate PC hardware blogger, and entrepreneur with extensive hands-on experience building and upgrading computers for gaming, productivity, and business operations.
As the founder of Vonebuy.com, a verified ecommerce store under Vietnam’s Ministry of Industry and Trade, I combine my technical knowledge with real-world business applications to help users make confident decisions.
I specialize in no-nonsense guides on RAM overclocking, motherboard compatibility, SSD upgrades, and honest product reviews sharing everything I’ve tested and implemented for my customers and readers.