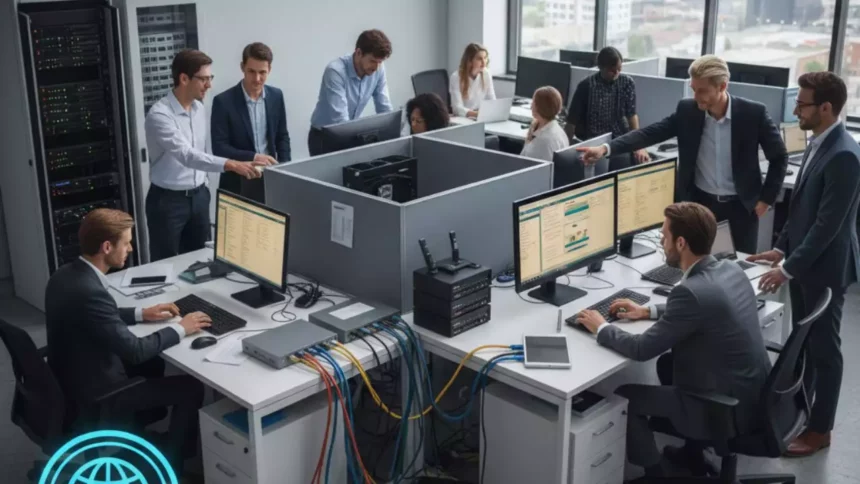
In today’s interconnected world, where data flows as freely as coffee in a busy office, understanding the backbone of our digital ecosystems is essential. If you’re reading this, you’re likely curious about Local Area Network (LAN), a technology that quietly powers homes, offices, and schools without much fanfare. Think of a LAN as the digital glue that connects your devices, allowing them to share files, printers, and even internet access in a confined space. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a small business owner, or just someone trying to troubleshoot your home Wi-Fi, this guide will break it all down for you. We’ll explore what a LAN is, how it works, its components, and why it’s still relevant in 2025, when everything from smart homes to remote work relies on seamless connectivity.
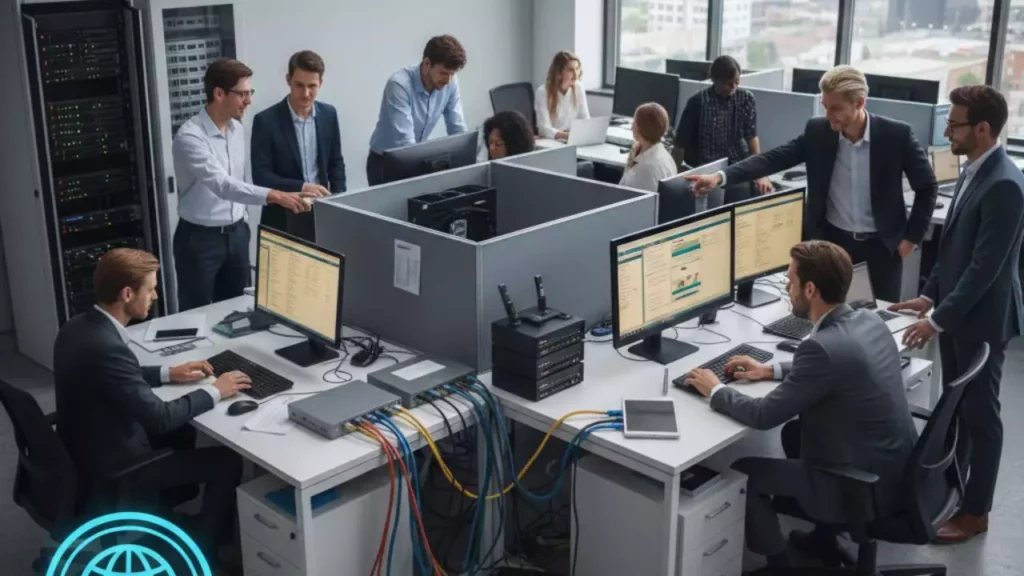

By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear, practical grasp of LANs, complete with real-world examples and tips for implementation. Let’s dive in and demystify this foundational networking concept.
What Exactly is a LAN?
At its core, a Local Area Network (LAN) is a system that links computers and other devices within a limited geographical area, such as a single building, office floor, or even a home. Unlike wider networks like the internet, which span vast distances, a LAN is all about local efficiency. It’s designed to enable fast, reliable communication between devices, making it ideal for sharing resources without relying on external infrastructure.
According to reliable sources, a LAN typically interconnects devices like computers, printers, and servers within a small radius, often just a few hundred meters. This setup allows for the distribution of data and the sharing of network devices, such as a central printer or file server. Imagine a small office where multiple employees can access the same documents or print jobs without emailing files back and forth; that’s the magic of a LAN.
LANs have been around since the early days of computing, evolving from simple wired connections to sophisticated wireless setups. In 2025, with the rise of hybrid work models and smart devices, LANs are more versatile than ever. They can be as basic as a home network connecting your laptop to your smart TV or as complex as a corporate setup with advanced security protocols. What makes a LAN “local” is its reliance on private infrastructure, managed by the users themselves, rather than public carriers like internet service providers.
One key aspect of a LAN is its speed and low latency. Because the network is confined to a small area, data travels quickly, often at speeds up to 10 gigabits per second with modern Ethernet standards. This is a far cry from the slower, more variable performance of wide area networks (WANs). For instance, in a school setting, a LAN could connect all classroom computers to a shared database, allowing teachers to update lesson plans in real time without delays.
The Evolution of LAN Technology
To truly appreciate what a LAN is today, it’s helpful to look back at its history. LANs emerged in the 1970s as businesses sought ways to connect computers for efficient data sharing. Early systems like Ethernet, developed by Xerox in the 1970s, laid the groundwork for modern networking. By the 1980s, companies like IBM and DEC were rolling out proprietary LAN solutions, but it wasn’t until the 1990s that standards like IEEE 802.3 made Ethernet the dominant protocol.
Fast-forward to 2025, and LAN technology has undergone significant transformations. Wireless LANs, or WLANs, using standards like Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7, have become the norm, offering speeds up to 40 Gbps and better handling of multiple devices. This evolution is driven by the explosion of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, think smart refrigerators, security cameras, and voice assistants, all needing to communicate seamlessly.
In recent years, advancements in fiber optics and Power over Ethernet (PoE) have enhanced LAN reliability. PoE, for example, allows devices like IP phones and security cameras to receive both data and power through a single Ethernet cable, simplifying installations in offices or homes. As we move into 2025, trends like edge computing are pushing LANs to integrate with cloud services, creating hybrid networks that blend local speed with global reach.
This evolution isn’t just technical; it’s practical. Businesses are using LANs for everything from video conferencing to virtual reality training, while homeowners leverage them for smart home automation. The key takeaway is that LANs have adapted to our changing needs, remaining a cornerstone of digital infrastructure.
Key Components of a LAN
Building a LAN involves several essential components, each playing a vital role in ensuring smooth operation. Let’s break them down, as understanding these elements will help you set up or troubleshoot your own network.
First, you have the hardware. At the heart of any LAN are the computers or devices that need to connect, such as desktops, laptops, or smartphones. These are linked via network interface cards (NICs), which act as the gateway for data transmission. In a typical setup, you’d also need switches and routers. A switch connects devices within the LAN, directing data packets efficiently, while a router manages traffic between the LAN and external networks, like the internet.
Cables are another crucial element. Traditional LANs use twisted pair cables (like Cat 5e or Cat 6) for wired connections, offering high speeds and security. For wireless LANs, access points broadcast signals, allowing devices to connect via Wi-Fi. Don’t forget about servers, which store and manage shared resources, such as files or applications.
According to expert insights, the main components include:
- Computers and devices: The endpoints that generate and receive data.
- Network devices: Like switches, routers, and access points, which handle data flow.
- Cables and connectors: Ensuring physical connections are secure and fast.
- Software and protocols: Operating systems and tools like TCP/IP that govern communication.
In a real-world scenario, a small business might use a switch to connect multiple workstations to a central server, with a router providing internet access. This setup not only boosts productivity but also allows for easy scalability as the business grows.
How LANs Work: The Basics of Data Transmission
Now that we’ve covered the components, let’s explore how a LAN actually functions. At its simplest, a LAN operates by transmitting data packets between connected devices using defined protocols. The most common is Ethernet, which uses a system called Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) to manage traffic and avoid conflicts.
Here’s how it works in practice: When you send a file from your computer to a printer on the same LAN, the data is broken into packets. These packets travel through the network via the switch, which determines the most efficient path. If it’s a wireless LAN, the access point handles the transmission over radio frequencies.
In 2025, with advancements in mesh networking, LANs can self-heal and expand coverage without a central point of failure. For example, in a large office, multiple access points might form a mesh, ensuring that even if one fails, the network remains operational.
Security is a big part of how LANs work today. Features like firewalls and encryption protocols (such as WPA3 for Wi-Fi) protect data from unauthorized access. This is especially important in environments like hospitals, where LANs handle sensitive patient information.
Types of LANs and Their Applications
LANs aren’t one-size-fits-all; they come in various types, each suited to specific needs. The most common is the Ethernet-based LAN, which uses wired connections for high-speed, reliable performance. Then there’s the wireless LAN (WLAN), popularized by Wi-Fi, which offers flexibility without the hassle of cables.
Another variant is the virtual LAN (VLAN), a logical segmentation of a physical LAN that enhances security and management. For instance, in a corporate setting, a VLAN could isolate the finance department’s network from the rest, preventing data breaches.
In real-world applications, LANs are everywhere. In education, they enable shared learning resources; in healthcare, they support electronic health records; and in retail, they power point-of-sale systems. By 2025, with the growth of 5G and edge computing, LANs are integrating with wider networks for applications like autonomous vehicles or smart cities.
To compare, let’s look at a simple table highlighting the differences between common LAN types:
| LAN Type | Key Features | Best For | Typical Speed Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wired Ethernet | High security, low latency | Offices and data centers | 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps |
| Wireless WLAN | Easy setup, mobile access | Homes and public spaces | 500 Mbps to 9.6 Gbps (Wi-Fi 7) |
| VLAN | Network segmentation, security | Enterprises and large organizations | Varies based on base LAN |
This table illustrates how choosing the right type depends on your environment’s needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LANs
Like any technology, LANs have their pros and cons. On the positive side, they offer high-speed data transfer, cost-effective resource sharing, and easy maintenance within a controlled area. For example, in a home office, a LAN allows you to stream 4K videos without buffering, all while keeping your data secure from external threats.
However, LANs aren’t without drawbacks. They can be vulnerable to internal attacks if not properly secured, and scaling them for larger areas might require additional hardware. In 2025, with increasing cyber threats, experts recommend regular updates to firmware and the use of intrusion detection systems to mitigate risks.
Despite these challenges, the benefits often outweigh the downsides, especially for small to medium-sized operations where a LAN can significantly boost efficiency.
Setting Up Your Own LAN: A Step-by-Step Guide
Ready to build a LAN? It’s easier than you might think. Start by assessing your needs: How many devices will you connect, and do you want wired or wireless? For a basic home LAN, you’ll need a router, a modem if you’re connecting to the internet, and devices with NICs.
Step 1: Choose your topology, star, ring, or bus, based on your setup. A star topology, with a central switch, is the most common for its reliability.
Step 2: Install cabling or set up access points. Use Cat 6 cables for wired connections to future-proof your network.
Step 3: Configure your devices using software like the router’s admin interface. Set up IP addresses and enable security features like passwords and firewalls.
Step 4: Test and troubleshoot. Use tools like ping commands to ensure everything connects properly.
In 2025, tools like automated network management software make setup even simpler, often with AI-driven optimization.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
LANs are the unsung heroes of modern life. In a corporate environment, they enable collaborative tools like shared drives and video calls. In education, LANs support interactive classrooms with shared screens and online resources. Even in entertainment, LAN parties for gaming rely on fast, local connections.
Consider a case study: A mid-sized retail chain uses a LAN to integrate their inventory system with point-of-sale terminals, reducing errors and improving stock management. This not only streamlines operations but also provides valuable data for business decisions.
Future Trends in LAN Technology
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, LANs are evolving with trends like 5G integration, enhanced AI for network optimization, and sustainable designs. For instance, energy-efficient PoE systems are reducing carbon footprints, while software-defined networking (SDN) allows for dynamic reconfiguration.
As remote work persists, LANs will increasingly blend with cloud services, offering the best of both worlds: local speed and global accessibility.
Security Considerations for LANs
In an era of rising cyber threats, securing your LAN is paramount. Implement encryption, use strong passwords, and regularly update firmware. Features like virtual private networks (VPNs) can add an extra layer of protection, especially for remote access.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a LAN and a WAN?
A Local Area Network (LAN) connects devices in a small area, like a home or office, with high speeds and local management. In contrast, a Wide Area Network (WAN), such as the internet, spans large geographical areas and relies on service providers for connectivity. Generally, LANs offer faster, more secure connections for internal use, while WANs are essential for external communication. This distinction is crucial for businesses deciding how to structure their networks.
How do I troubleshoot common LAN issues?
If your LAN is experiencing problems, start by checking physical connections like cables and power sources. Use diagnostic tools such as ping or ipconfig to test connectivity. In most cases, issues stem from outdated firmware or interference in wireless setups. For wireless LANs, ensure your access point is placed away from obstacles and restart devices to resolve temporary glitches.
Can a LAN work without the internet?
Yes, a LAN can function independently of the internet. It’s designed for local device communication, such as sharing files or printers within a network. However, for tasks requiring external access, like browsing websites, you’ll need a connection via a router. In 2025, many LANs are hybrid, seamlessly integrating with the internet for added functionality.
What are the speed limitations of a LAN?
LAN speeds vary by technology; wired Ethernet can reach up to 10 Gbps or more, while wireless options like Wi-Fi 7 offer up to 40 Gbps. Factors like distance and interference can reduce actual speeds. Typically, for optimal performance, keep devices within 100 meters of the central switch or access point.
Is a LAN secure for sensitive data?
LANs can be secure if properly configured with features like firewalls and encryption. However, internal threats, such as unauthorized access from within the network, are a risk. Experts recommend using multi-factor authentication and regular security audits to protect data, especially in environments like healthcare or finance.
How does a LAN support remote work?
In 2025, LANs support remote work by integrating with VPNs and cloud services, allowing secure access from outside the local network. For example, employees can connect to the office LAN via a secure tunnel, accessing shared resources as if they were on-site. This setup enhances productivity while maintaining data security.
What hardware do I need for a home LAN?
For a basic home LAN, you’ll need a router, switches if connecting multiple devices, and Ethernet cables for wired setups. Wireless options require a compatible access point. Choose hardware based on your needs, like supporting smart devices or high-speed gaming, to ensure a reliable network.
Are LANs still relevant with cloud computing?
Absolutely, LANs remain essential even with cloud computing. They provide the local infrastructure for fast data processing and reduce latency for applications like video editing. In many cases, LANs act as a bridge to the cloud, offering a secure, efficient way to handle data before it reaches external servers.

Hi, I’m Nghia Vo: a computer hardware graduate, passionate PC hardware blogger, and entrepreneur with extensive hands-on experience building and upgrading computers for gaming, productivity, and business operations.
As the founder of Vonebuy.com, a verified ecommerce store under Vietnam’s Ministry of Industry and Trade, I combine my technical knowledge with real-world business applications to help users make confident decisions.
I specialize in no-nonsense guides on RAM overclocking, motherboard compatibility, SSD upgrades, and honest product reviews sharing everything I’ve tested and implemented for my customers and readers.