Graphics cards are essential for everything from gaming to professional 3D rendering, pushing your computer to new heights of visual performance. However, like any hardware component, graphics cards can encounter issues that disrupt their functionality. Whether you’re a gamer or a professional, a malfunctioning graphics card can be frustrating. This article explores common symptoms of a faulty graphics card and provides practical solutions to get it back in working order.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty Graphics Card
Poor Gaming Performance
You’ve invested in a new gaming laptop or GPU expecting blazing-fast frame rates, but the performance falls short by 30% or more. While slight variations in frame rates can stem from multiple factors, consistently underperforming GPUs warrant further investigation.
System Crashes
A faulty graphics card can cause various system crashes, such as blue screen errors, random freezes without a blue screen, unexpected reboots, or sudden shutdowns. If your system logs indicate graphics driver issues, the GPU is likely the culprit.
Visual Artifacts on Screen
Graphics cards are responsible for rendering visuals on your screen. When they malfunction, you may notice strange visual effects, such as distorted colors, stretched 3D models, or flickering displays, indicating potential hardware issues.
Loud Fan Noise
If your graphics card’s fan sounds like a jet engine during 3D applications or even at startup, it could signal a problem. Excessive fan noise often indicates overheating or hardware stress.
Driver Issues
Occasional black screens followed by a notification that the graphics driver has crashed and recovered are a common symptom of driver-related issues. Frequent occurrences can disrupt your workflow or gaming experience.
Black Screen
In some cases, a graphics card may fail entirely, resulting in a black screen with no visual output. Testing with an integrated GPU or a spare graphics card can help determine if the GPU is at fault.
How to Fix a Graphics Card Not Working
Before replacing your graphics card, try these troubleshooting steps to diagnose and potentially resolve the issue.
Ensure the GPU Is Enabled
This is particularly relevant for laptops but can also apply to desktops with integrated GPUs. Many laptops disable dedicated GPUs when unplugged to save battery life, and this setting may persist even when plugged in.
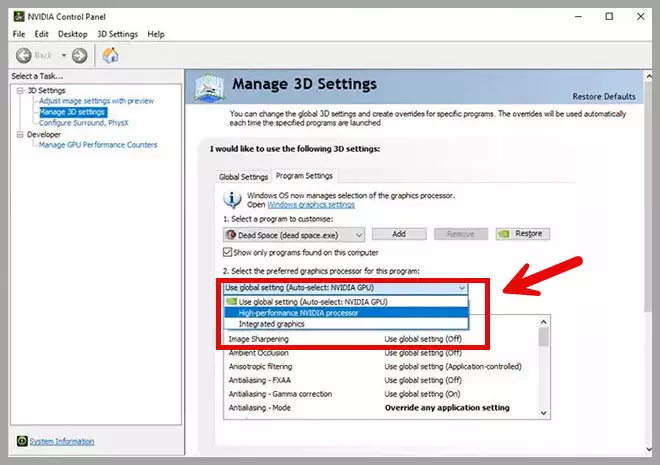
How to Enable the GPU:
- For Nvidia GPUs: Open the Nvidia Control Panel, navigate to “Manage 3D Settings,” and select the “Program Settings” tab. Choose the affected game or application, then select “High-performance NVIDIA processor” from the dropdown menu.
- Laptop-Specific Software: Some laptops, like ASUS models, include software (e.g., Armoury Crate) to toggle the GPU. Disable “iGPU mode” to enable the dedicated GPU permanently.
- BIOS Settings: Access your laptop’s BIOS (usually by pressing F2 or F8 during startup) and check for options to enable the dedicated GPU or disable the integrated GPU.
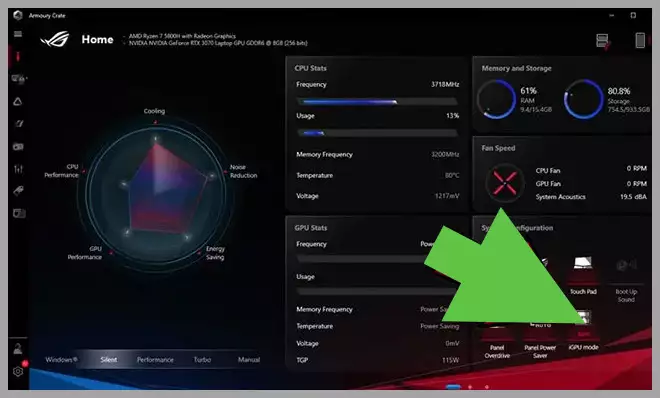
Some laptops offer their own software that allows you to enable and disable the GPU 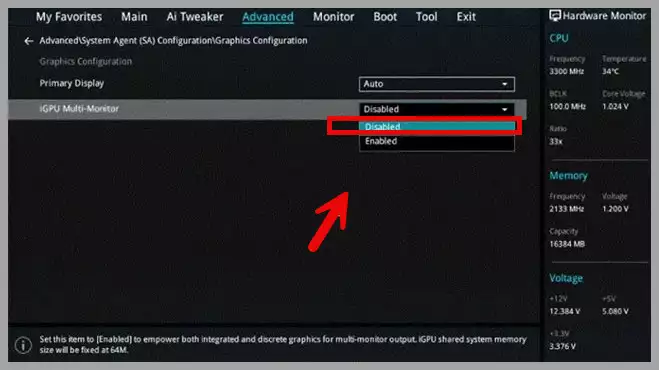
Enable graphics card in BIOS
Switch Graphics APIs
If issues occur in specific games, the problem might be related to the graphics API (DirectX, OpenGL, or Vulkan). Most modern games allow you to switch APIs in advanced graphics settings. For example, older GPUs like the Nvidia GTX 970 may struggle with newer APIs like Vulkan, causing visual issues. Switching to a different API, such as OpenGL, can resolve compatibility problems.
Update or Roll Back Drivers
Outdated or incompatible drivers can cause performance issues or system instability. Conversely, newer drivers may not always be optimized for older GPUs.
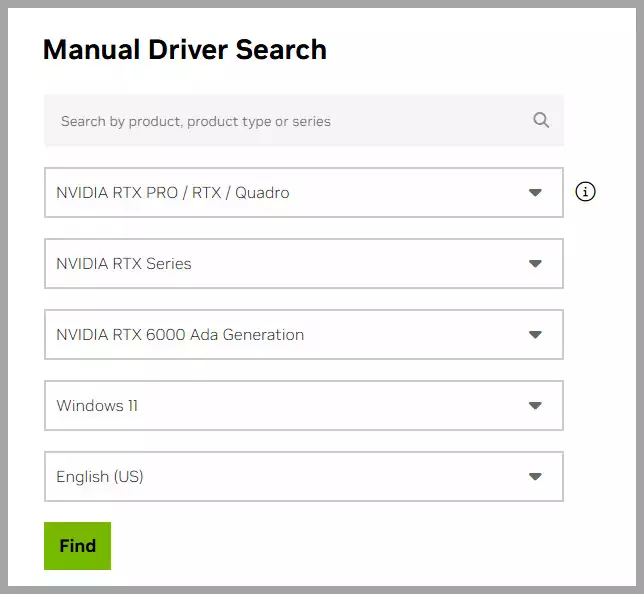
Steps to Manage Drivers:
- Update Drivers: Visit the Nvidia, AMD, or Intel website to download and install the latest drivers for your graphics card.
- Roll Back Drivers: If issues started after a driver update, revert to an older driver version via the manufacturer’s driver archive.
Remove Old Drivers Completely
When upgrading GPUs or switching brands (e.g., from AMD to Nvidia), residual driver files can cause conflicts. Use Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) to remove all traces of previous drivers:
- Download DDU from a trusted source.
- Run DDU to clean out existing drivers.
- Restart your PC and install the new drivers or swap GPUs.
This process ensures a clean slate, eliminating driver-related conflicts.
Address Overheating
Overheating is a common cause of graphics card issues, especially if errors occur during intensive tasks or if the fan is excessively loud.
Steps to Cool Your GPU:
- Clean the GPU: Remove the graphics card and clean dust from the fans and heatsink using compressed air. Avoid opening the card unless you’re experienced, as replacing thermal paste can be complex.
- Use Software Tools: Tools like MSI Afterburner allow you to monitor GPU temperatures and adjust fan speeds for better cooling.
- Improve Case Cooling: Ensure case fans are clean and unobstructed. Check cable management to avoid blocking airflow.
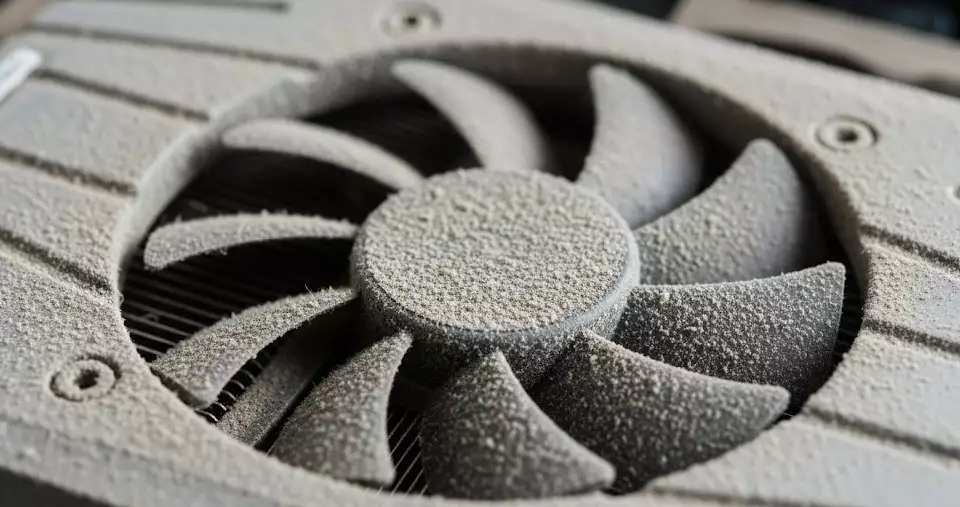

Cooling fan is dirty
Verify Proper Installation
A loose graphics card or power connector can cause issues. Ensure the GPU is securely seated in its PCI slot and that all required power connectors are firmly plugged in.
Check Video Cables
Faulty or loosely connected video cables (HDMI, DisplayPort, etc.) can cause visual artifacts. Verify that cables are securely connected or replace them to rule out cable issues.
Test the Monitor
Visual issues may stem from a faulty monitor rather than the GPU. Test your setup with a different monitor to isolate the problem.
Inspect the Power Supply Unit (PSU)
An underpowered or failing PSU may not deliver sufficient power to the GPU, causing errors during high-demand tasks like gaming or 3D rendering. Test the GPU with a different PSU to confirm if the power supply is the issue. If confirmed, consider upgrading to a PSU with adequate wattage and stability.
Replace the Graphics Card
If none of the above solutions work, the graphics card may be irreparably damaged. Test with a low-cost replacement card to confirm the issue. If the new card resolves the problem, it’s time to invest in a new, high-quality GPU.
Conclusion
A malfunctioning graphics card can disrupt your gaming or creative workflow, but many issues can be resolved with proper troubleshooting. From enabling the GPU to updating drivers and addressing overheating, these steps can save you from prematurely replacing your card. If all else fails, consider testing with a spare GPU or upgrading to a new model to restore optimal performance.
For more tech tips and troubleshooting guides, stay tuned to our blog!
FAQ
Why is my graphics card not detected by the system?
How do I know if my GPU is dead or just not working properly?
Can a dirty graphics card cause it to stop working?
What should I do if my graphics card fans are not spinning?
Why is my monitor showing “No Signal” when the GPU is installed?
Could driver issues cause my GPU to malfunction?
Is my power supply causing GPU problems?
Does overheating cause permanent damage to the graphics card?
How can I fix screen artifacts or strange colors?

Hi, I’m Nghia Vo: a computer hardware graduate, passionate PC hardware blogger, and entrepreneur with extensive hands-on experience building and upgrading computers for gaming, productivity, and business operations.
As the founder of Vonebuy.com, a verified ecommerce store under Vietnam’s Ministry of Industry and Trade, I combine my technical knowledge with real-world business applications to help users make confident decisions.
I specialize in no-nonsense guides on RAM overclocking, motherboard compatibility, SSD upgrades, and honest product reviews sharing everything I’ve tested and implemented for my customers and readers.



![The detailed guide to installing a second SSD in your computer [Full A Z]](https://ohhmua.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/The-detailed-guide-to-installing-a-second-SSD-in-your-computer-Full-A-Z.webp)
![Comprehensive Computer Beep Codes [Help You Fix Errors]](https://ohhmua.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Comprehensive-Computer-Beep-Codes-Help-You-Fix-Errors.webp)