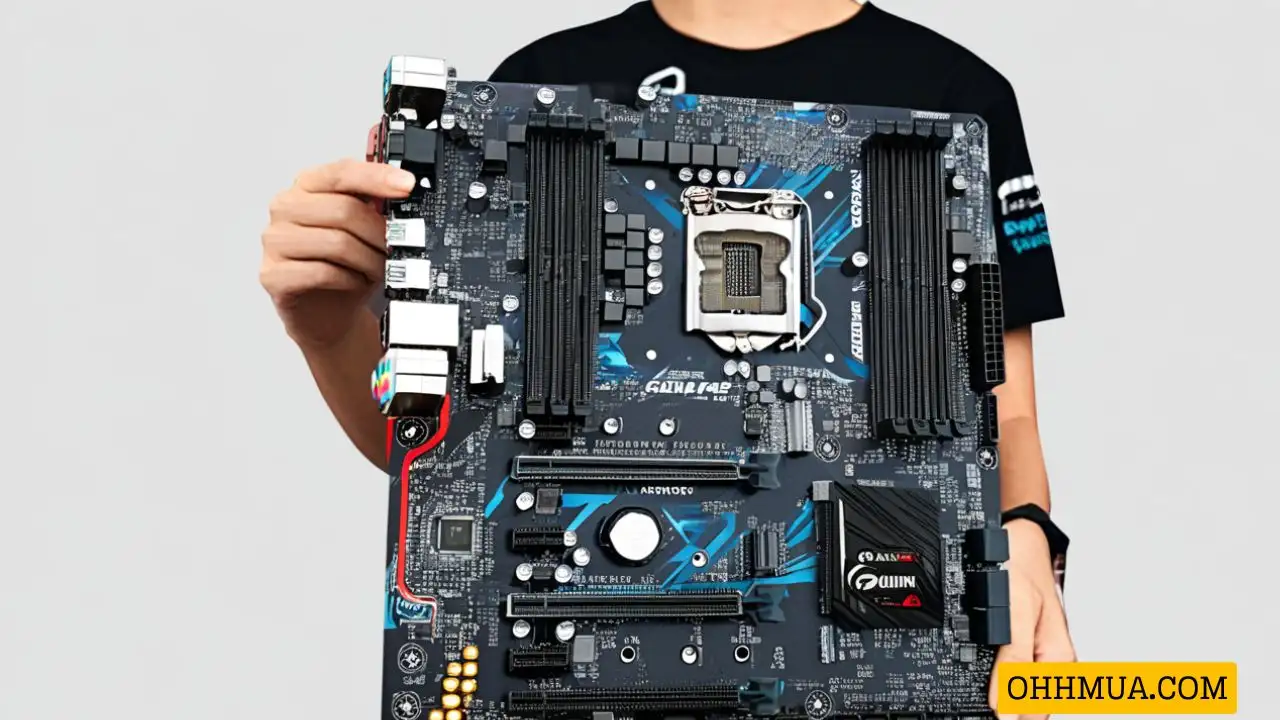
What is Computer Hardware?
Computer hardware refers to the physical components of a computer system. It encompasses all the tangible parts that you can touch and see, in contrast to software, which consists of the programs and data that run on the hardware. Hardware can be classified into internal and external components.
What Are Internal Hardware Components?
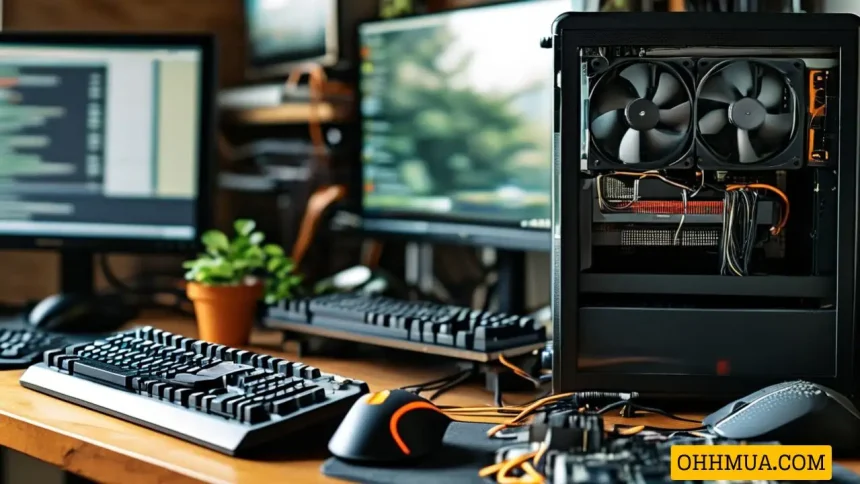
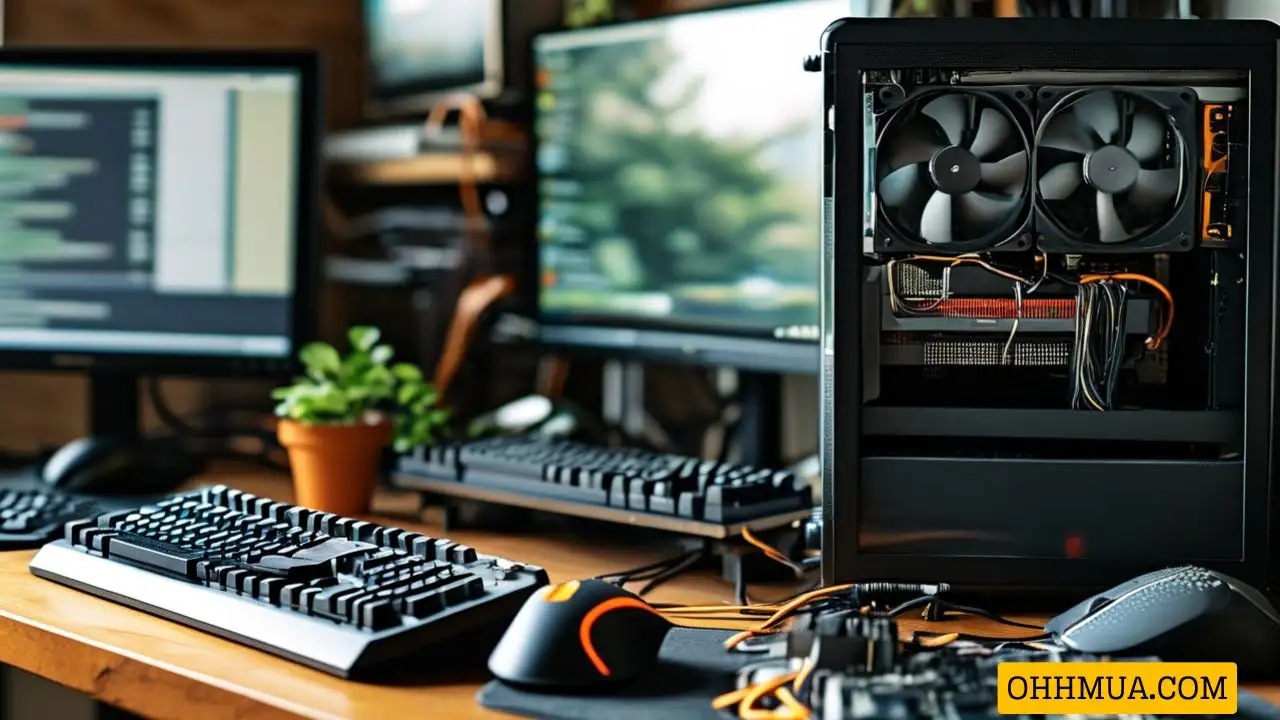
Internal hardware components include the motherboard, central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), hard drive, optical drive, cooling system, power supply unit (PSU), transistors, chips, graphics processing unit (GPU), network interface card (NIC), and Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports. These components handle or store information provided by programs or the operating system (OS). Below is a diagram illustrating the internal computer hardware components.
Diagram of Internal Computer Hardware
External Hardware Components
External components, also known as peripherals, are devices that are usually connected to the computer to control its input or output. Common input devices include the mouse, keyboard, microphone, camera, touchpad, stylus, control keys, scanner, USB drives, or memory cards. Output devices include monitors, printers, speakers, and headphones. All these hardware devices are designed to “provide instructions” to the executing software. Here are some examples of peripheral components.
Hardware Virtualization
Hardware virtualization is the abstraction of physical computing resources from the software using those resources. This is done by a virtual machine manager (VMware), also known as a hypervisor. Essentially, the hypervisor creates virtual hardware instances (using real hardware resources to create virtual hardware systems) so that system resources can be shared and used more efficiently. In cloud computing, hardware virtualization is often combined with infrastructure as a service (IaaS).
Learn about virtualization and VMware
Types of Hardware
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the central “backbone” connection point of the computer, allowing all internal components and external peripherals to connect. It is the main printed circuit board in the computer and contains critical components such as the CPU, RAM, power supply, graphics card, and sound card.
- CPU: The CPU is responsible for processing most of the computer’s data, turning input into output.
- RAM: RAM stores the operating system, application programs, and data currently in use, so the device’s processor can quickly access and process them. It is the computer’s main memory and reads and writes faster than other storage types, including hard drives (HDD), solid-state drives (SSD), and optical drives. RAM is “volatile,” meaning data remains in RAM while the computer is on but is lost when the computer is turned off. The operating system and other files are reloaded into RAM, usually from an SSD or HDD, when the computer is restarted.
- Monitor: The monitor can be an external screen or integrated into the computer.
- HDD: A non-volatile storage device, HDD stores operating system files, application data, media, and other documents. HDDs can store data permanently, even during power outages.
- SSD: A type of non-volatile storage device that stores data continuously on solid-state flash memory. SSDs include a flash controller and NAND flash memory and do not have moving parts like HDDs. SSDs are significantly faster than traditional mechanical hard drives and use less power, which extends battery life in laptops.
- Graphics Card: Responsible for rendering graphics in the computer and displaying information on the screen, the graphics card aims to reduce the “burden” on the processor or RAM.
- Power Supply: The power supply converts electrical power from the outlet into usable power for the other internal components of the computer.
Conclusion
In this article, I have introduced what computer hardware is. If you have any questions, please leave a comment below. Thank you and see you in the next articles!

Hi, I’m Nghia Vo: a computer hardware graduate, passionate PC hardware blogger, and entrepreneur with extensive hands-on experience building and upgrading computers for gaming, productivity, and business operations.
As the founder of Vonebuy.com, a verified ecommerce store under Vietnam’s Ministry of Industry and Trade, I combine my technical knowledge with real-world business applications to help users make confident decisions.
I specialize in no-nonsense guides on RAM overclocking, motherboard compatibility, SSD upgrades, and honest product reviews sharing everything I’ve tested and implemented for my customers and readers.