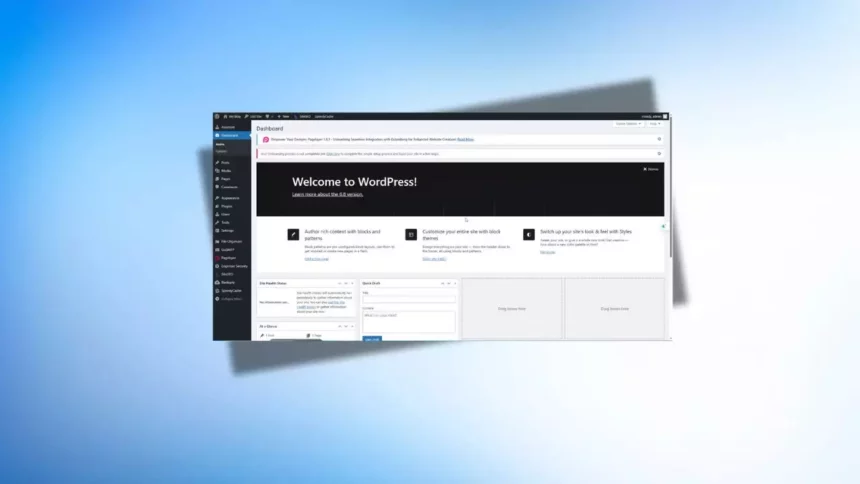
WordPress is one of the most popular content management systems (CMS) used for building websites and blogs. The WordPress Dashboard is the first screen you see after logging into your WordPress admin area. It serves as the control center for managing the content, design, and functionality of your website. Let’s dive into the key features of the WordPress Dashboard and explain its various tools and sections in detail.
1. The WordPress Dashboard Overview
When you log into WordPress, you’ll land on the Dashboard screen. The Dashboard is divided into several sections that give you quick access to all the major functions of your WordPress website. Here are the key elements:
-
Welcome to WordPress Section: This is a quick overview section where you can find resources and guides to help you get started with WordPress.
-
Quick Draft: Located on the left side, the “Quick Draft” box allows you to quickly add a new post draft. Simply type in your title and content, and save it as a draft for later editing.
-
Site Health Status: This area provides an overview of your site’s performance and health. It will notify you of any critical issues with the site such as outdated plugins or security risks.
-
At a Glance: This section gives you a quick summary of your website’s content, including the number of posts, pages, and comments.
2. The Left Sidebar Menu
On the left side of the Dashboard, you’ll find the main navigation menu. Here’s an overview of the main sections:
-
Posts: This section allows you to manage your posts. You can create new posts, edit existing ones, and organize posts by categories and tags.
-
Media: The “Media” section is where you can upload and manage your images, videos, and other media files.
-
Pages: You can create and manage static pages (such as “About Us” or “Contact”) in this section. Pages are typically used for content that doesn’t change often.
-
Comments: This section allows you to manage comments left by visitors on your posts. You can approve, reply to, or delete comments.
-
Appearance: This is where you can change the design of your WordPress site. You can choose themes, customize the look of your website, and add widgets.
-
Plugins: In this section, you can install, activate, and manage plugins to extend the functionality of your site. Plugins are third-party add-ons that enhance your WordPress website.
-
Users: This section allows you to manage users who have access to your site. You can add new users, assign them different roles (Administrator, Editor, Author, etc.), and control permissions.
-
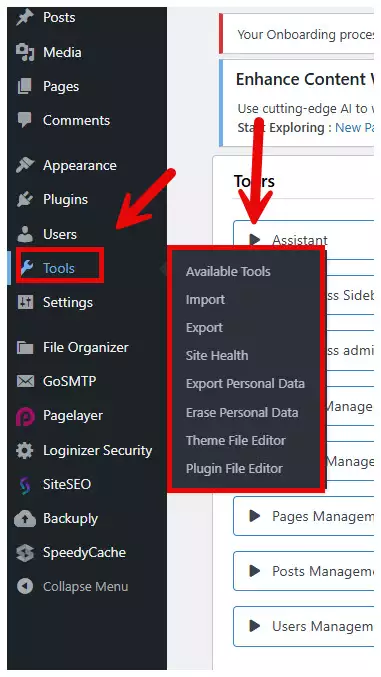
Tools: The tools section offers utilities for managing your website. It includes options for importing and exporting content, as well as some advanced settings.
tools wordpress dashboard The Tools section in WordPress offers a variety of utilities designed to help you manage your website. It includes options for importing and exporting content, as well as some advanced settings to ensure your site runs smoothly. Below is a breakdown of the tools available in this section:
-
Available Tools
This section provides an overview of all the tools available by default in WordPress or added through plugins. It gives you quick access to different utilities that help you manage various aspects of your site. -
Import
The Import tool allows you to bring content from other platforms or WordPress installations into your website. Whether you’re migrating content from another website or platform, this tool helps transfer posts, pages, categories, tags, and other content types seamlessly to WordPress. -
Export
The Export tool is used to back up or move your content from WordPress to another site. This tool allows you to export posts, pages, media, and other content types into an XML file. You can then import this file into another WordPress site or a different platform. -
Site Health
The Site Health tool monitors the performance, security, and overall health of your WordPress site. It runs periodic checks to ensure your site is running optimally, offering recommendations for improvements such as updating plugins, themes, or WordPress itself. It also generates a report detailing potential risks or issues that could affect your site’s speed, security, or overall performance. -
Export Personal Data
The Export Personal Data tool helps you comply with privacy regulations such as GDPR by allowing you to export user data stored on your WordPress site. When a user requests access to their personal data, this tool enables you to generate a report containing their personal information, including email, comments, and other user-generated content. -
Erase Personal Data
In line with data protection policies, the Erase Personal Data tool enables you to delete personal data of users when requested. This feature ensures compliance with privacy laws, giving users control over their data. It allows you to permanently remove user details, including personal information, comments, and other stored data. -
Theme File Editor
The Theme File Editor tool provides access to the code of your active WordPress theme. From here, you can edit various theme files such as the header, footer, CSS, and PHP files. This tool is ideal for users who want to customize their website’s appearance or functionality at the code level. However, it is recommended to use a child theme to avoid losing customizations during theme updates. -
Plugin File Editor
Similar to the Theme File Editor, the Plugin File Editor allows you to access and edit the code of your installed plugins. You can make changes to a plugin’s code, but this tool is recommended only for advanced users as any errors in the code could break your site. It is advised to test any changes in a staging environment before applying them to the live site.
-
-
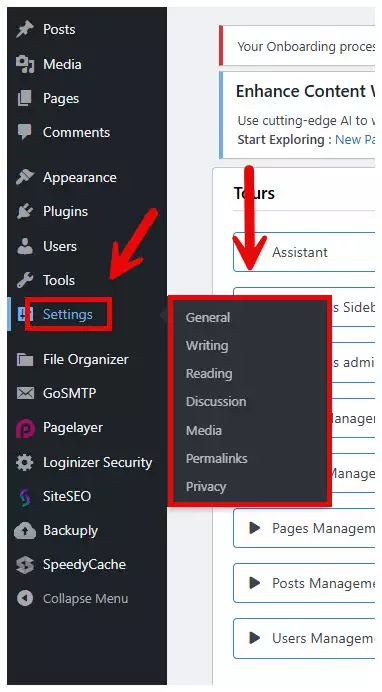
Settings: This is where you configure the general settings for your site, such as site title, tagline, time zone, and more. You can also manage discussion settings, permalinks, and other important configurations.
settings wordpress dashboard The Settings section in WordPress is where you can configure the overall functionality and behavior of your website. This section allows you to adjust key aspects such as site title, time zone, user roles, discussion settings, media management, and more. Let’s explore each subsection in detail.
-
General Settings
The General settings allow you to configure your site’s basic information. Here you can set:
-
Site Title: The name of your website.
-
Tagline: A brief description or slogan for your site.
-
WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL): These are the URLs that point to your WordPress site.
-
Email Address: This is where notifications from your WordPress site will be sent.
-
Membership: Allow anyone to register as a user on your site.
-
Timezone, Date Format, Time Format: Configure the site’s timezone, and how dates and times are displayed.
-
Writing Settings
The Writing settings allow you to customize how you create and manage content. Key options include:
-
Default Post Category: Choose the default category for posts.
-
Default Post Format: Set the default format for your posts (standard, aside, gallery, etc.).
-
Post via Email: Allows you to post content by sending an email to a specific address (rarely used today).
-
Remote Publishing: Options for publishing posts remotely using protocols like XML-RPC.
-
Reading Settings
The Reading settings control how your content is displayed on the front end of the website. Key settings include:
-
Your homepage displays: Choose whether your site shows your latest posts or a static page as the homepage.
-
Blog pages show at most: Set the maximum number of posts to be displayed on blog pages.
-
Syndication feeds: Control how many items appear in your RSS feed.
-
For each article in a feed: Decide whether to display the full text or summary of each post in the feed.
-
Discussion Settings
The Discussion settings control how comments are handled on your site. You can manage:
-
Default article settings: Whether users are allowed to post comments or trackbacks on new articles.
-
Other comment settings: Control comment moderation rules, such as whether users must be registered or if their comments need to be approved before appearing.
-
Email me whenever: Choose whether you want to receive notifications when new comments are posted or when comments are held for moderation.
-
Media Settings
The Media settings control how images and other media files are handled on your site. Here you can set:
-
Image sizes: Configure default sizes for thumbnail, medium, and large images uploaded to your site.
-
Uploading files: Manage how media is organized in folders and set the default way media is displayed.
-
Permalinks Settings
The Permalinks settings are used to define the structure of your URLs. You can select from various options like:
-
Plain: Simple numeric URLs.
-
Day and name: URLs that include the date and title of the post.
-
Month and name: URLs that include the month and title of the post.
-
Post name: Clean URLs that display only the post title.
This setting is important for SEO, as more descriptive, readable URLs are better for search engines and user experience.
-
Privacy Settings
The Privacy settings allow you to manage your site’s privacy policy. You can set:
-
Privacy Policy Page: Select a page for your privacy policy, ensuring your site complies with privacy regulations like GDPR.
-
Personal Data: You can also use this section to manage the collection of personal data from users.
-
3. The Toolbar
The WordPress Toolbar is located at the top of the screen and provides quick access to essential functions:
-
Dashboard: Clicking on “Dashboard” will bring you back to the main admin screen.
-
Site Name/Logo: You can click on your site’s name or logo in the upper-left corner to view your website’s front-end or access the customizer to adjust the look and feel of your site.
-
Updates: This area will notify you when WordPress core, themes, or plugins have updates available. Keeping everything updated ensures your website is secure and runs smoothly.
-
Comments: A quick link to see any new comments that have been left on your posts or pages.
-
User Profile: Clicking on your username gives you access to your profile settings, where you can update your personal information, change your password, and adjust other settings related to your WordPress account.
4. The Editor
When creating content, WordPress provides two types of editors:
-
Block Editor (Gutenberg): WordPress’s default editor is block-based. This means that content is structured as “blocks” (text, images, videos, buttons, etc.). The Block Editor makes it easy to drag and drop various elements to create rich content.
-
Classic Editor: Some users prefer the traditional editor, which allows for a more familiar, WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editing experience. If you are used to this interface, you can still use it by installing the Classic Editor plugin.
5. Themes and Customization
The Appearance section allows you to manage the theme of your site. Themes control the overall design and layout of your website. WordPress comes with default themes, but you can easily install custom themes from the Theme Directory or upload premium themes.
Once you select a theme, the Customizer allows you to make live changes to your site, including adjusting colors, fonts, logos, and menus. You can preview these changes before publishing them.
6. Widgets and Menus
-
Widgets: These are small blocks of content that can be placed in various areas of your site, such as sidebars and footers. Examples include recent posts, categories, and social media links.
-
Menus: You can create custom navigation menus that help visitors easily find their way around your site. WordPress allows you to add pages, posts, and custom links to your menus.
7. Managing Plugins
Plugins are essential for adding extra features to your WordPress site. The Plugins section allows you to browse, install, activate, and update plugins. There are thousands of plugins available to add features such as contact forms, SEO tools, security measures, and much more.

Hi, I’m Nghia Vo: a computer hardware graduate, passionate PC hardware blogger, and entrepreneur with extensive hands-on experience building and upgrading computers for gaming, productivity, and business operations.
As the founder of Vonebuy.com, a verified ecommerce store under Vietnam’s Ministry of Industry and Trade, I combine my technical knowledge with real-world business applications to help users make confident decisions.
I specialize in no-nonsense guides on RAM overclocking, motherboard compatibility, SSD upgrades, and honest product reviews sharing everything I’ve tested and implemented for my customers and readers.